-
2017
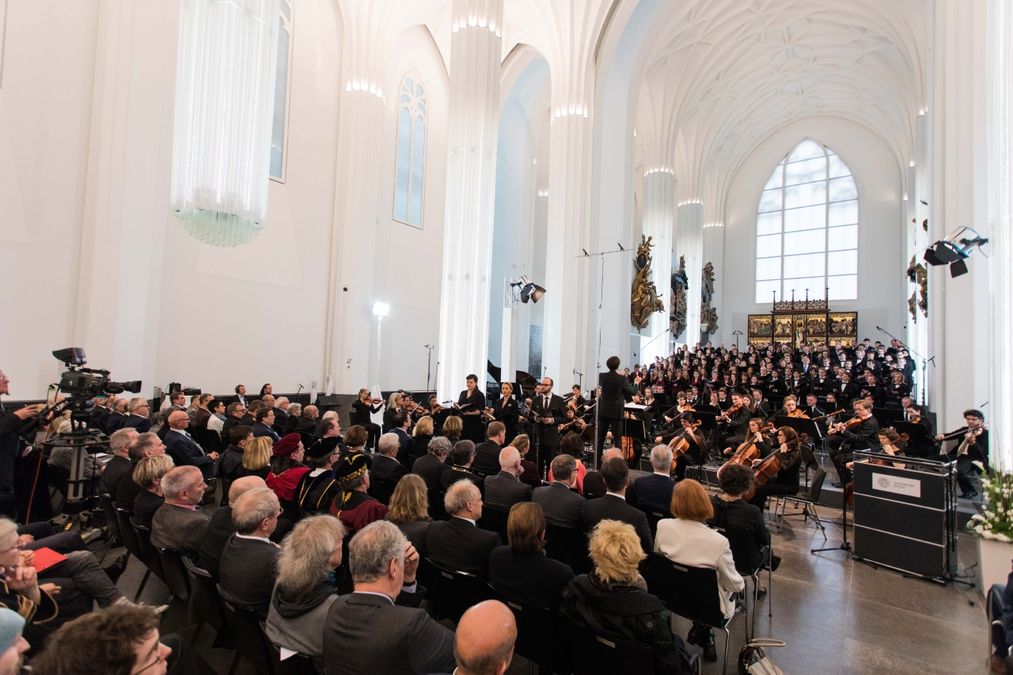
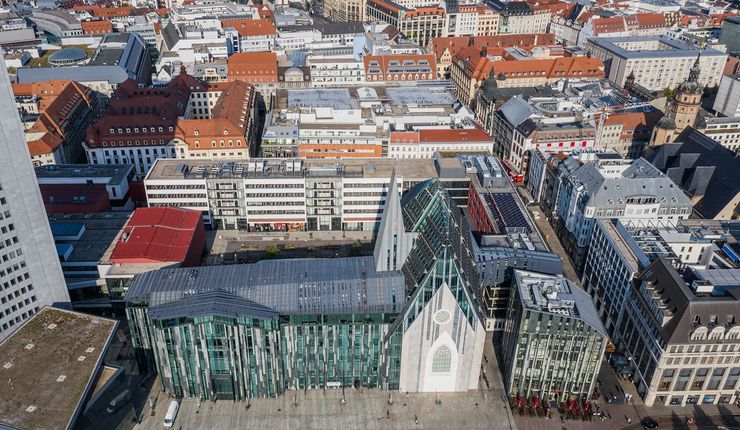
A ceremony marks the inauguration of Leipzig University’s Paulinum – Assembly Hall and University Church of St Paul.
-
2011
The Neues Augusteum is presented to the public on 2 December.
On 1 March, Professor Beate Schücking becomes the first woman in the history of our university to take up the office of rector.
-
2009
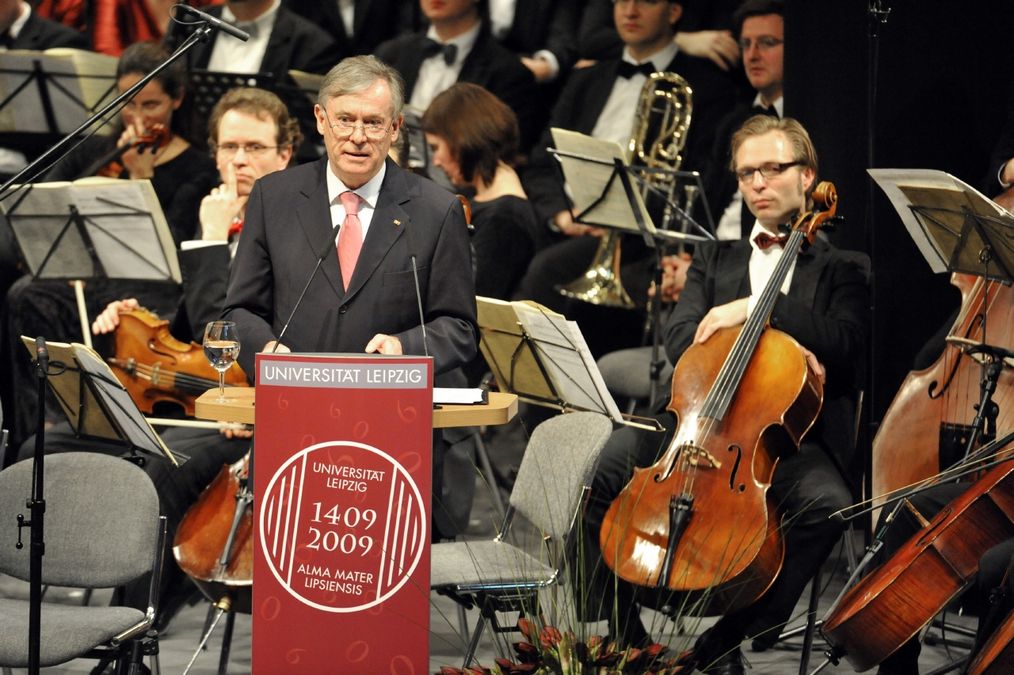
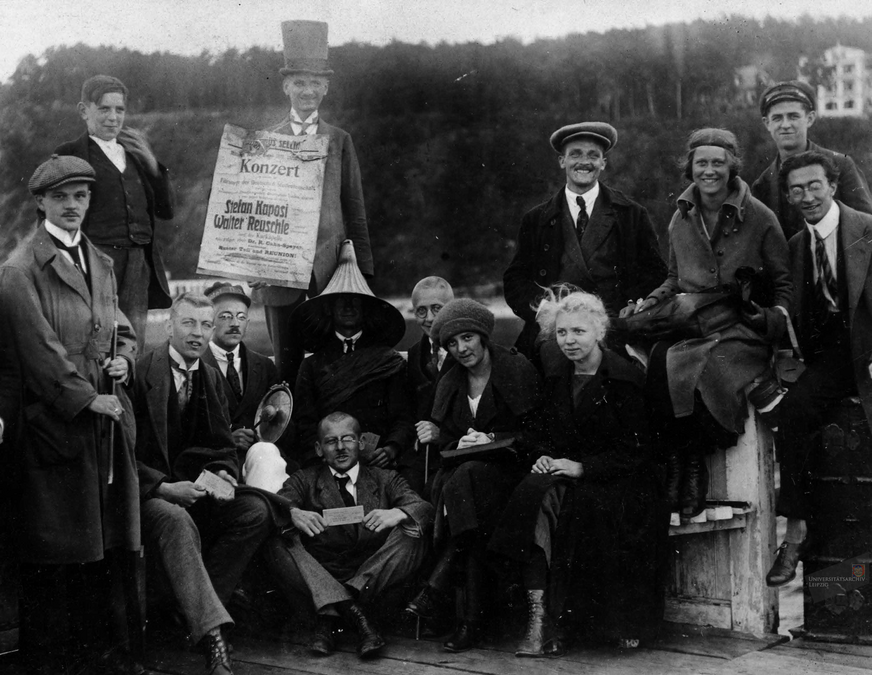
600 years of Leipzig University: the highlight of the anniversary year is a ceremony on 2 December with an address by then Federal President Horst Köhler.
First cross-faculty alumni meeting at Leipzig University
-
2001
Announcement of an EU-wide architectural competition for the new and redesigned inner-city university complex on Augustusplatz
-
1990–1994
Having been renamed “Karl-Marx-Universität” in the GDR, the University drops this new name after German reunification and returns to its traditional faculty and institute structure.
-
1989–1990
Many members of the University take to the streets of Leipzig to demonstrate for freedom and civil rights. Students set up a democratically legitimate students’ union.
-
1973
The new skyscraper on Augustusplatz is handed over to the Karl-Marx-Universität on 31 August.
-
1971
The new main building is handed over to the Karl-Marx-Universität on 3 September.
-
1968
In the course of the third higher education reform in the GDR, the traditional faculty and institute structures are dissolved and Sektionen are founded.
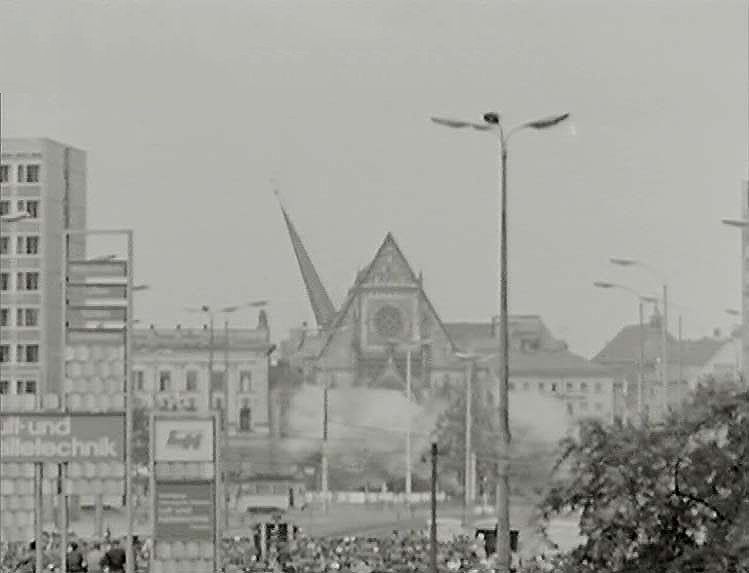
Demolition of St Paul’s University Church, which remained unscathed in the Second World War, on 30 May following a decision by the Politburo and Leipzig city assembly
-
1953
The Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) decides to rename the Universität Leipzig “Karl-Marx-Universität Leipzig”
-
1946
Reopening of Leipzig University in the Capitol cinema by the Soviet military administration
-
1933–1945
National Socialism brings intellectual life in Leipzig to a standstill. Many employees and students are dismissed, imprisoned or killed. Most of the buildings on Augustusplatz are destroyed towards the end of the Second World War.
-
1932
Werner Heisenberg, head of the Institute of Theoretical Physics at Leipzig University, is awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics.
-
1927
Paul Flechsig is awarded the first professorship for brain research in Germany.
-
1906
For the first time, women are officially admitted to study at Leipzig University.
-
1899
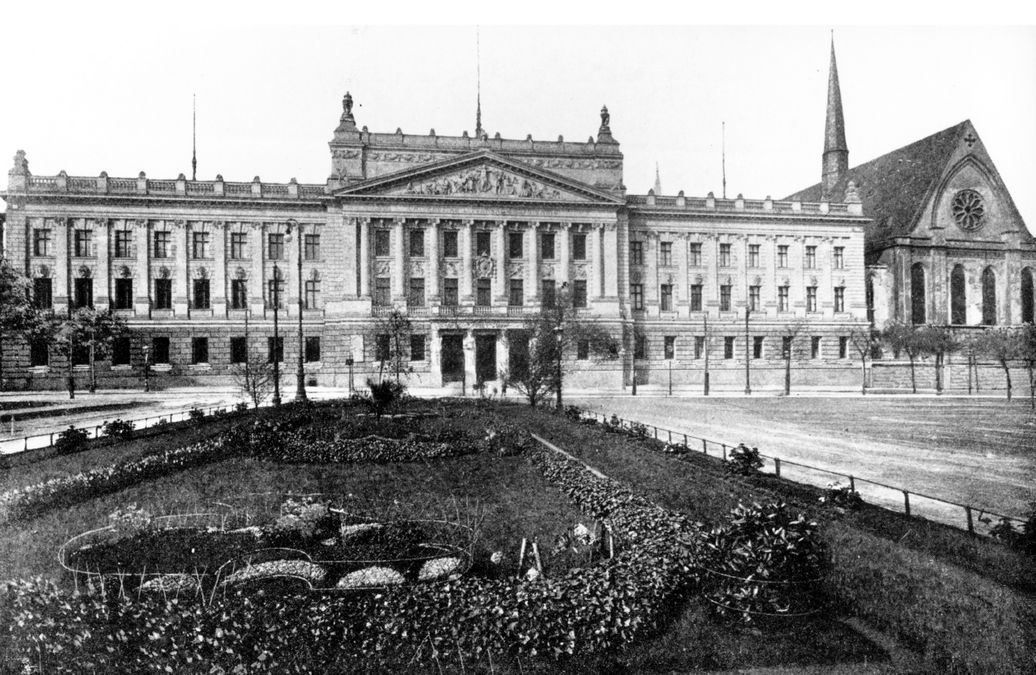
Inauguration of St Paul’s University Church, redesigned by Arwed Roßbach in the neo-Gothic style
-
1897
Inauguration of the Augusteum on Augustusplatz, remodelled by Arwed Roßbach in the Renaissance Revival style.
-
1879
Wilhelm Wundt opens the world’s first institute of experimental psychology at Leipzig University.
-
1836
Ceremonial inauguration of the neoclassical Augusteum built by Albert Geutebrück on the square in front of the Grimmaisches Tor (from 1839 Augustusplatz).
-
1813
During the Battle of Leipzig, the University is used as a military hospital.
-
1765–1768
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe studies law at Leipzig University.
-
1687
Christian Thomasius is the first German university professor to give a lecture in German.
-
1682
Germany’s first scholarly journal, Acta Eruditorum, is published in Leipzig.
-
1661
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz enrols at Leipzig University.
-
1544
Duke Maurice of Saxony transfers the former Dominican monastery to the University as the Collegium Paulinum. This along with other material support makes Leipzig one of the wealthiest universities in the Holy Roman Empire.
-
1543
Founding of Leipzig University Library
-
1539
The Reformation marks the beginning of a new phase in the history of the University. The work of Rector Caspar Borner and humanist Joachim Camerarius is tantamount to the founding of a new university.
-
1519
Leipzig Debate: the disputation between theologian Johann Eck and the reformers Martin Luther, Andreas Karlstadt and Philipp Melanchthon marks the nascent break between Rome and the Lutherans.
-
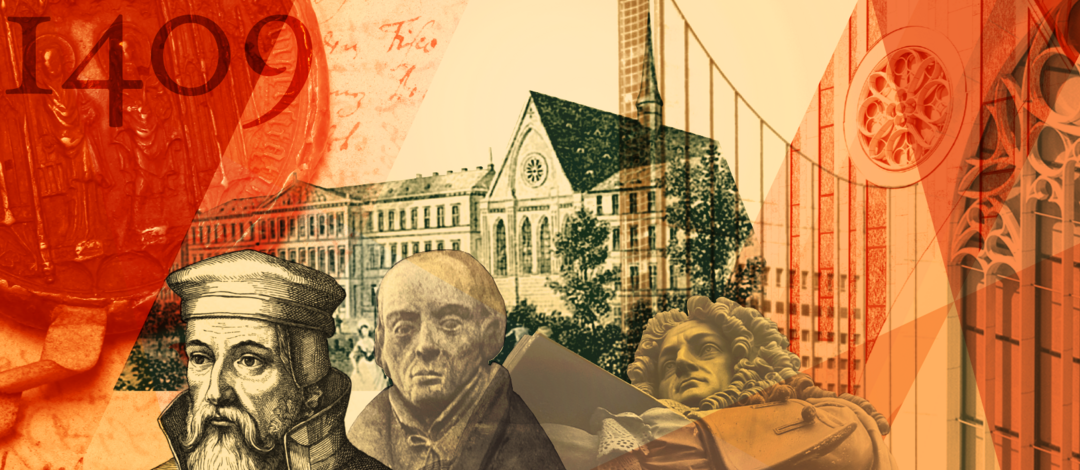
1409
The Universität Leipzig is founded as part of the monastery (Stift) of St Thomas on 2 December with former masters and scholars from Prague.